NASA eyes "chain mail" fabric for use in space
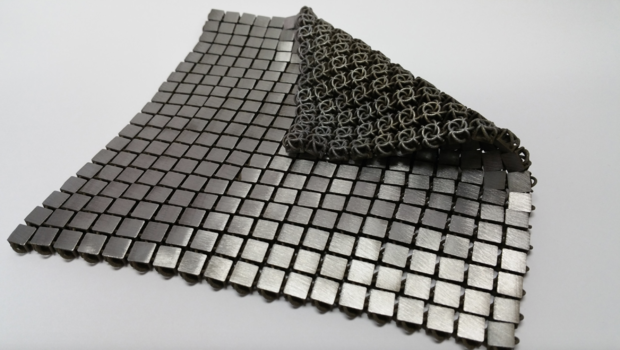
To protect its spacecraft from the rigors of deep space, a team of NASA engineers is turning to a time-honored — and battle-proven — solution: chain mail. Led by Raul Polit Casillas, whose mother is a fashion designer in Spain, the group at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) has developed a prototype fabric that puts an extraterrestrial spin on the armor of yore.
The fabric is strung together from a series of articulated metallic tiles, which reflect light on one side and absorb it on the other, providing a mechanism for thermal regulation. Pliable yet durable, it can also be manipulated into a variety of shapes without ceding tensile strength.
That versatility makes the material well-suited for a range of potential applications — shielding objects deployed in space from debris, say, or insulating space suits for astronauts, JPL researchers said in a statement. Future explorers could even use it to pave over unstable alien terrain without melting the ice beneath. [Cosmic Threads: Astronauts Inspire Space-Age Fashion]
Unlike its medieval counterpart, which involved linking together tiny rings of hand-forged steel, JPL's take employs the far less laborious process of 3D printing — or 4D, depending on whom you ask.
"We call it '4-D printing' because we can print both the geometry and the function of these materials," Polit Casillas said in the statement. "If 20th century manufacturing was driven by mass production, then this is the mass production of functions."
Additive manufacturing — basically 3D printing on an industrial scale — makes the process of creating novel materials cheaper and easier. And that's even without taking into account future leaps and bounds in technology.
The quick turnaround, in particular, makes tinkering with designs a cinch.
"We are just scratching the surface of what's possible," said Andrew Shapiro-Scharlotta, whose office at JPL funds research for emerging technologies like Polit Casillas' fabric. "The use of organic and non-linear shapes at no additional costs to fabrication will lead to more efficient mechanical designs," he added in the statement.
Equally flexible is the composition of the fabric itself. For their prototype, Polit Casillas and his colleagues used standard 3D-printer grist: plastic filaments that are melted and deposited in layers, then exposed to UV light to fuse them into shape.
Future astronauts, on the other hand, may make do with found materials such as the native soil of other worlds or by recycling cast-off hardware. After all, squandering resources is a luxury you can ill afford when you're light-years from Earth, Polit Casillas said.
But even those of us on terra firma today can imbue objects with unique functionalities beyond the structural.
An aluminum plate with a heat-radiating design, for instance, is far more useful than one without.
"I can program new functions into the material I'm printing," Polit Casillas said. "That also reduces the amount of time spent on integration and testing. You can print, test and destroy material as many times as you want."
Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.